Designing for Database Security: Access Controls and Encryption
The hidden patterns that separate robust systems from security disasters
The Access Control Paradox: Why RBAC Breaks at Scale
The Encryption Layering Strategy: Beyond TLS
The Key Management Dilemma: Where Security Models Break
Real-World Implementation: The FAANG Approach
The Performance Security Trade-off: Measurement and Optimization
Practical Implementation: Building a Secure Database Layer
Expected Script Output Walkthrough
Key Verification Points
Experimenting to Deepen Understanding
Security Monitoring: The Observability Imperative
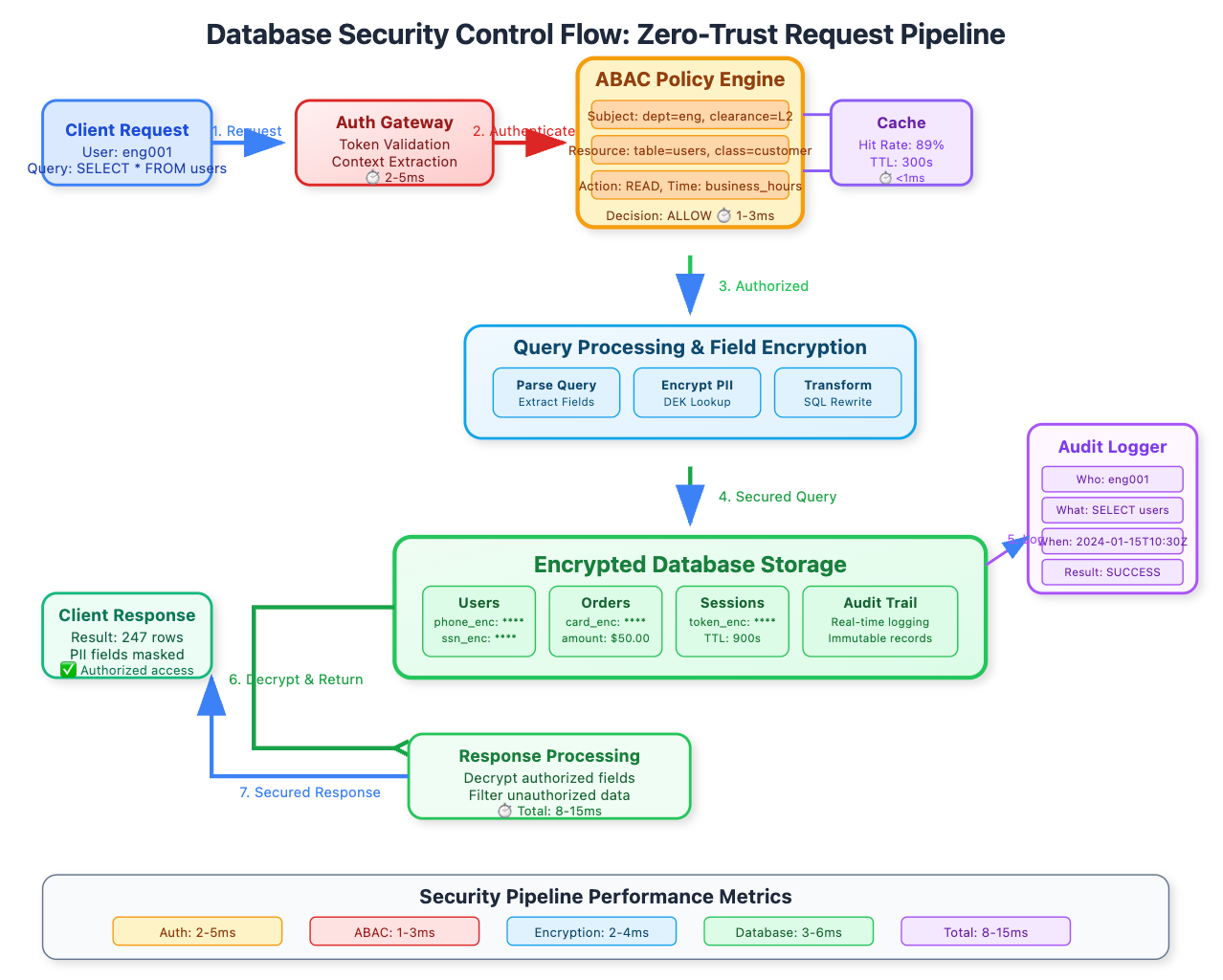
The Future of Database Security: Zero-Trust Architecture
Your Next Implementation Step
Traditional database security assumes a controlled perimeter, but distributed systems shatter that assumption. Today's database security isn't about building higher walls—it's about architecting systems that remain secure even when those walls inevitably crumble.
The uncomfortable truth? Most database security implementations fail not because of sophisticated attacks, but because engineers misunderstand the fundamental tension between access control granularity and system performance at scale.