Rolling Deployments: Strategies and Patterns
Issue #125: System Design Interview Roadmap • Section 5: Reliability & Resilience
Working Code Demo:
What You'll Master Today
Rolling deployment mechanics and why they're superior to big-bang releases
Advanced rollout strategies including canary integration and traffic shaping
Hidden failure patterns that can turn gradual deployments into system-wide outages
Production-grade health checking that prevents bad deployments from spreading
The Gradual Revolution
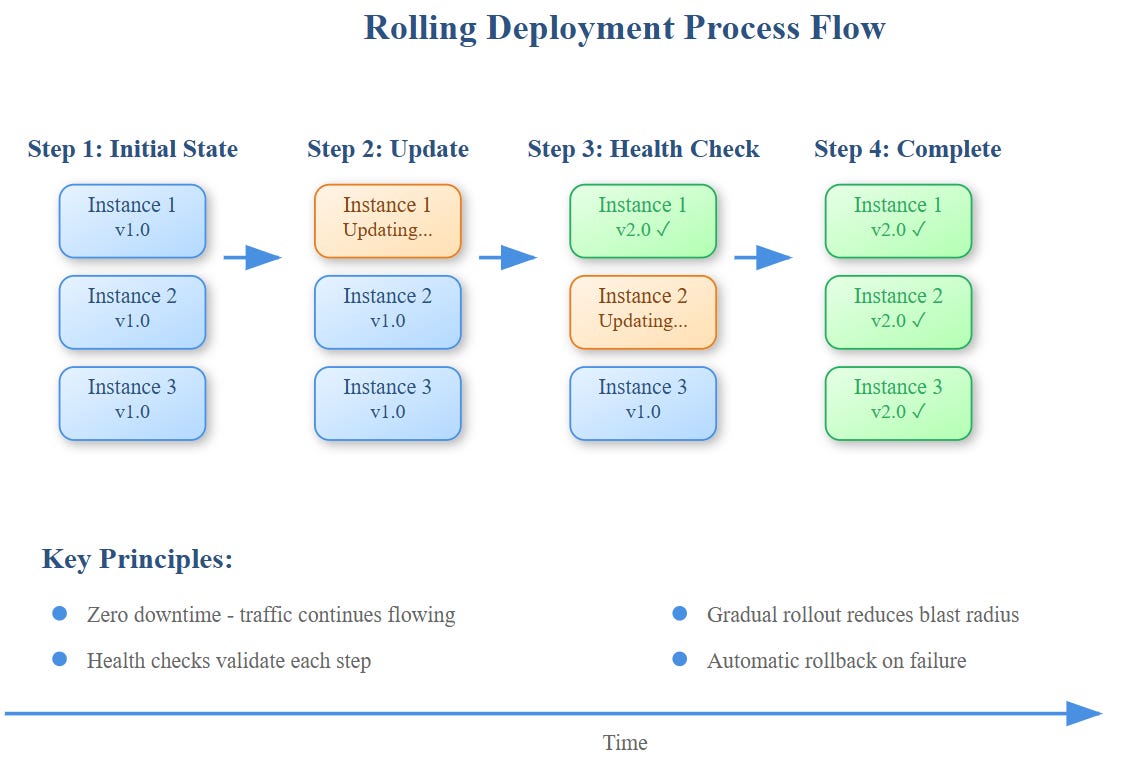
Rolling deployments represent the difference between jumping off a cliff and walking down a slope. Instead of replacing all instances simultaneously (big-bang deployment), you update them incrementally, maintaining service availability while monitoring each step.
Think of it like renovating a busy restaurant—you keep serving customers while upgrading one section at a time, ensuring you can always fall back to the working areas if something goes wrong.
Core Strategies: Beyond Simple Instance Replacement
1. Percentage-Based Rollouts
Most teams start with simple "replace 25% every 5 minutes" strategies, but production systems require more sophistication:
Rolling Strategy:
maxUnavailable: 1 # Never lose more than 1 instance
maxSurge: 1 # Add 1 extra during transition
updateBatch: 20% # Update 20% at a time
healthCheckGracePeriod: 60s
The hidden insight: batch size directly impacts blast radius. Large batches deploy faster but spread failures wider. Netflix uses dynamic batch sizing—starting with 1% for new services, scaling to 25% for proven stable services.
2. Dependency-Aware Sequencing
Rolling deployments must respect service dependencies. Updating a database schema before application code can break everything in between.
The pattern: dependency-first ordering where downstream services update before upstream consumers. Kubernetes operators automate this through resource ordering and readiness gates.
3. Traffic-Aware Scheduling
Smart rolling deployments consider traffic patterns. Updating instances during peak hours reduces available capacity when you need it most.
Production insight: time-box deployments around traffic valleys. Spotify deploys during European nights to minimize user impact, using automated scheduling based on traffic forecasts.
Advanced Patterns: Where Rolling Deployments Excel
Circuit Breaker Integration
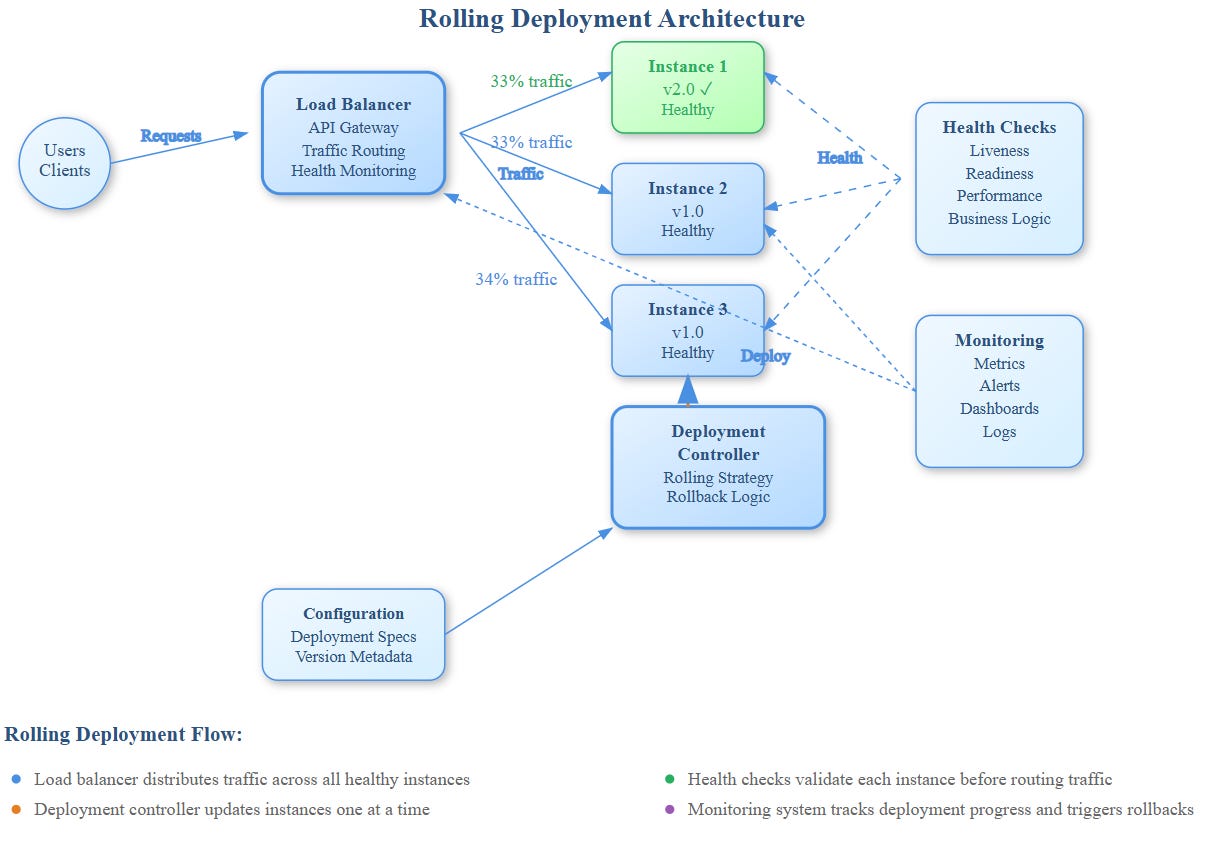
Rolling deployments should integrate with circuit breakers to prevent bad code from cascading. When new instances fail health checks, circuit breakers can automatically route traffic back to stable versions.
def rolling_health_check(instance):
if circuit_breaker.is_open():
return False # Don't promote unhealthy instances
return instance.health_check() and performance_check(instance)
Progressive Traffic Shifting
Beyond simple instance replacement, modern rolling deployments gradually shift traffic percentages:
5% traffic → New instance for 5 minutes
25% traffic → Monitor error rates and latency
100% traffic → Full promotion if metrics are healthy
This approach catches issues that only appear under real load, something static health checks miss.
Hidden Failure Modes: What Can Go Wrong
The Thundering Herd Problem
When all instances restart health checks simultaneously, they can overwhelm downstream dependencies. The solution: staggered health check initialization with random delays.
Memory Leak Amplification
Rolling deployments can mask gradual memory leaks. Each new instance starts with fresh memory, hiding the fact that long-running instances would eventually crash.
Monitor memory growth rates across instance lifecycles to catch this pattern early.
Configuration Drift During Rollouts
If configuration changes between the start and end of a rolling deployment, some instances may have different settings. Use configuration snapshots that lock config for the entire rollout duration.
Real-World Implementations
Kubernetes Rolling Updates
Kubernetes provides sophisticated rolling update controls through deployment specifications:
spec:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 25%
maxSurge: 25%
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
The key insight: progressDeadlineSeconds prevents stuck deployments from hanging indefinitely, automatically triggering rollbacks after timeout.
AWS ECS Rolling Deployments
ECS integrates rolling deployments with Application Load Balancers for seamless traffic management:
New tasks register with ALB
Health checks verify readiness
Traffic gradually shifts to new tasks
Old tasks drain connections before termination
Google Cloud Run Gradual Rollouts
Cloud Run's traffic splitting enables percentage-based rollouts without infrastructure management:
gcloud run services update-traffic myservice \
--to-revisions=new-revision=10,old-revision=90
This approach lets you test new code with real traffic while maintaining majority stability.
Production Implementation Insights
Health Check Design
Effective rolling deployments require multi-layer health checking:
Liveness checks: Is the process running?
Readiness checks: Can it handle traffic?
Business logic checks: Are core features working?
The pattern: Start with shallow checks for fast feedback, then deeper validation before full traffic routing.
Rollback Automation
Rolling deployments should include automatic rollback triggers:
Error rate exceeds baseline by 3x
Latency P95 increases by 50%
Health check failure rate > 20%
Implement these as deployment policies, not manual reactions.
Observability Integration
Every rolling deployment needs comprehensive monitoring:
@monitor_deployment
def rolling_update():
for batch in deployment_batches:
deploy_batch(batch)
wait_for_health()
validate_metrics()
if anomaly_detected():
rollback_immediately()
break
Track deployment velocity, failure rates, and MTTR to optimize your rollout strategies over time.
Your Production Checklist
Before implementing rolling deployments:
✅ Define health check criteria that catch real problems
✅ Set up automated rollback triggers based on business metrics
✅ Plan dependency update ordering to avoid compatibility issues
✅ Configure traffic shaping for gradual load introduction
✅ Implement comprehensive monitoring throughout the rollout process
Hands-On Challenge
Build a rolling deployment system that can update a 3-instance web service with zero downtime. Include health checks, traffic routing, and rollback capabilities. Measure how long deployments take and what failure scenarios your system can handle.
The demo implementation below provides a complete working example you can experiment with and extend for your own systems.
GitHub Link:
https://github.com/sysdr/sdir/tree/main/Rolling_Deployments/rolling-deployment-demoNext week in Issue #126, we'll explore Tenant Isolation in Multi-Tenant Systems, building on the deployment strategies we've learned to ensure one tenant's updates don't impact others.